Littelfuse PolySwitch and POLY-FUSE devices are Polymeric Positive Temperature Coefficient (PPTC) devices which offer a resettable overcurrent protection alternative, thereby reducing warranty, service and repair costs. Ideal for situations where frequent overcurrent conditions occur or constant uptime is required, resettable PPTCs are typically used in consumer electronics, power line, telecom, I/O port, process control and medical equipment protection applications.
PPTCs increase resistance as temperature increases due to increased flow. Designed to limit unsafe currents while allowing constant safe current levels, resistance will "reset" automatically when the fault is removed and temperature returns to a safe levels.
Surface mount resettable PPTC devices provide overcurrent protection for applications where space is at a premium and resettable protection is desired. Package size varies from 0402 to 3425, while hold current ranges from 50mA to 7.0A. LoRho, 0603L, 0805L, 1206L, 1210L, 1812L, 2016L, 2920L, 250S, femtoSMD, picoSMD, nanoSMD, microSMD, miniSMD, decaSMD, SMDC, AHS, SMD, nanoAMSD, microASMD, miniASMD, ASMD.
Radial leaded resettable PPTCs are designed to provide overcurrent protection for applications where space is not a concern and resettable protection is preferred. USBR, 16R, 30R, 60R, 72R, 250R, 600R, RGEF, RUEF, RXEF, RHEF, RKEF, AGRF, AHRF, AHEF.
Battery strap resettable PPTCs provide reliable, non-cycling protection against overcharging and short circuits events for rechargeable battery cells where resettable protection is desired. VLR, VLP, VTP, MXP, MGP, SRP, LR4, RSD.
New Littelfuse Lo Rho resettable PPTCs offers ultra-low normal operating resistance while maintaining the same performance of other Littelfuse PPTC products and are available in Surface Mount Low Rho SMD Series and Surface Mount Lo Rho Series.
The Telecom resettable PPTC Series is designed to protect against short-duration high-voltage fault currents (power cross or power induction surge) typically found in telecommunications and networking applications. The 250R, 250S, TRF250, TSL250, TS250, TCF250 and TSV250 series can be used to help telecom networking equipment meet the protection requirements specified in ITU K.20 and K.21. The 600R, TRF600, TR600, TS600 and TSM600 series is designed to be used in applications that need to meet the requirements of GR–1089-CORE and UL60950/ EN60950/IEC60950.
Littelfuse plants for PolySwitch devices are ISO/TS 16949:2009 and ISO 9001:2008 certified.
Traditional Fuses vs. PPTCs
Fuses and PPTCs are both overcurrent protection devices, though each offer their own unique operating characteristics and benefits. Understanding the differences between the two technologies should make the choice in selection easier, depending on the application.
The most obvious difference is that PPTCs are automatically resettable whereas traditional Fuses need to be replaced after they they are tripped. Whereas a fuse will completely stop the flow of current (which may be desired in critical applications) after most similar overcurrent event, PPTCs continue to enable the equipment to function, except in extreme cases.
Because they reset automatically, many circuit designers choose PPTCs in instances where overcurrent events are expected to occur often, and where maintaining low warranty and service costs, constant system uptime, and/or user transparency are at a premium. They are also often chosen in circuits that are difficult to access or in remote locations, were fuse replacement would be difficult.
There are several other operating characteristics to be considered that distinguish PPTCs and fuses, and it is also best to test and verify device performance before use within the end application.
To learn more about traditional fuses versus PPTCs click here.
PPTC Characteristics and Terms
Overcurrent circuit protection can be accomplished with the use of either a traditional fuse or PPTC (positive temperature coefficient) device. PPTCs are typically used in a wide variety of telecom, computer, consumer electronics, battery and medical electronics product applications where overcurrent events are common and automatic resettability desired.
Littelfuse offers PPTCs with the following general forms and features, and come in a variety of sizes and capacities:
- A full range of compact footprints
- Low hold current
- Very fast trip time
- Low resistance
- Protection devices up to 600Vdc
- A very high hold current
- Low trip-to-hold current ratio
- Low resistance
- A narrow low profile design
- A weldable band Nickel terminal
- Low resistance–for extended battery run time
If your application requirements fall outside of our product range, in certain instances we can offer customized solutions. Please contact Littelfuse for more information.
Littelfuse PPTC Characteristics
Both Polymeric (Positive Temperature Coefficient) PPTC and traditional Fuse devices react to heat generated by the excessive current flow in a circuit. A fuse melts open, interrupting the current flow whereas a PPTC limits current flow as it rises in temperature, changing from low to high resistance state. In both cases this condition is called "tripping." The graph at right shows the typical response of a PPTC to temperature.
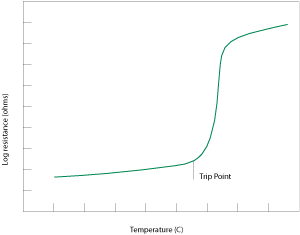
Littelfuse Polymer PPTCs are made chiefly of high density polyethylene mixed with graphite. During an overcurrent event, a Polymer PPTC will heat and expand, which in turn causes the conducting particles to break contact and stop the current.
The general procedure for resetting the device after an overload has occurred is to remove power and allow the device to cool down.
Leakage Current
When a PPTC is in a "tripped state" it protects the circuitry by limiting the current flow to a low leakage level. Leakage current can range from less than a hundred milliamps (mA) at rated voltage up to a few hundred milliamps (mA) at lower voltages. Fuses on the other hand completely interrupt the current flow when tripped, and this open circuit results in no leakage current when subjected to an overload current.
Interrupting Rating
PPTCs are rated for a maximum short circuit current at rated voltage also known as "breaking capacity" or Imax. This fault current level is the maximum current that the device can withstand safely, keeping in mind that the PPTC will not actually interrupt the current flow (see Leakage Current above). A typical Littelfuse PPTC short circuit rating is 40A; or for the battery strap PPTCs, this value can reach 100A. Fuses do in fact interrupt the current flow in response to the overload and the range of interrupting ratings, vary from tens of amperes (A) up to 10,000 (A) amperes at rated voltage.
Operating Voltage Rating
General use Littelfuse PPTCs are not rated above 60V while fuses are rated up to 600V.
Hold Current Rating
The hold (operating) current rating for PPTCs can be up to 14A, while the maximum level for fuses can exceed 30A.
Resistance
Reviewing product specifications indicates that similarly rated PPTCs have about twice (sometimes more) the resistance of fuses.
Agency Approvals
Littelfuse PPTCs are Recognized under the Component Program of Underwriters Laboratories to UL Standard 1434 for Thermistors. The devices have also been certified under the CSA Component Acceptance Program.
Time-Current Characteristic
Comparing the time-current curves of PPTCs to time-current curves of fuses show that the speed of response for a PPTC is similar to the time delay of a Littelfuse Slo-Blo® fuse.
Temperature Rerating
The useful upper limit for a PPTC is generally 85°C, while the maximum operating temperature for fuses is 125°C.
Ambient temperature effects are in addition to the normal rerating. PPTCs hold and trip rating must be rerated when applied at conditions other than room ambient. For example, any rise in ambient temperature will decrease the hold current rating as well as the trip current. A reduction in ambient temperature will increase the trip current as well as the hold current.
The temperature rerating curves in the table below compare PPTCs to fuses and illustrate that more rerating is required for a PPTC at a given temperature.
Temperature Rerating Curves Comparing PPTCs to Fuses
|
| Chart Key |

|
Curve A
Thin-Film Fuses and 313 Series (.010 to .150A)
Curve B
FLAT-PAK® , Nano2® , PICO® , Blade Terminal,
Special Purpose and other leaded and cartridge fuses
(except 313.010 – .150A)
Curve C
Resettable PPTCs |
PPTCs are typically used as circuit protection in applications where sensitive components are at constant risk of damage from overcurrent conditions. The ability of PPTCs to reset themselves after exposure to a fault current makes them ideal within circuits that are not easily accessible to a user or technician or where constant uptime is required.
Typical applications include port protection on personal computers (USB, Firewire, keyboard/mouse, and serial ports), peripherals (hard drives, video cards, and hubs), cell phone, battery packs, industrial controls, lighting ballast and motor controls.
The chart below is meant as a quick guide in narrowing to a Littelfuse PPTC device that may be appropriate to certain end applications.
For detailed application assistance please visit our Application Design Center Site.
| |
SURFACE MOUNT |
| |
|
LoRho |
0603L |
0805L |
1206L |
1210L |
1812L |
2016L |
2920L |
250S |
| Telecom |
| Ul60950 ,TIA-968-A, GR-1089 Req's |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
| ITU-T Recoomendations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
| CPE (Customer Premises Equipment) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
| Analog Line Card |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
| T1/E1/J1 And HDSL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
| ISDN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
| ADSL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
| Cable Telephony |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
| PBX/KTS And Key Telephone System |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
| Computer |
CPU |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
|
| USB |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
| IEEE1284 Parallel Data Bus |
|
|
|
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
| IEEE 802.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
✗ |
|
| IEEE 1394 |
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
|
✗ |
|
| I/O Ports |
|
|
|
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
|
✗ |
|
| PC Card |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
|
✗ |
|
| SCSI |
|
|
|
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
|
✗ |
|
| Video Port |
|
|
|
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
|
✗ |
|
| HDMI / LCD Monitor |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
Consumer
Electronics |
Set Top Box |
|
|
|
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
|
✗ |
|
| Loudspeaker |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Smart Card Reader |
|
|
|
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
| Mobile Phone |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
| Linear AC/DC Adapter |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
|
✗ |
|
| Portable Electronic Input Port |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
| Electromagnetic Loads, Motor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
✗ |
|
| Solenoid Protection |
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
|
✗ |
|
Medical
electronic |
Voltage / Current Input Terminal |
|
|
|
✗ |
|
✗ |
|
|
|
| |
RADIAL LEADED |
BATTERY STRAP |
| |
|
USBR |
16R |
30R |
60R |
72R |
250R |
600R |
LR |
LT |
SL |
ST |
VL |
VT |
| Battery |
Lithium Cell |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
| Battery Pack |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
| |
Ul60950 ,TIA-968-A, GR-1089 Req's |
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ITU-T Recoomendations |
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| CPE (Customer Premises Equipment) |
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Analog Line Card |
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| T1/E1/J1 And HDSL |
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ISDN |
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ADSL |
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Cable Telephony |
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| PBX/KTS And Key Telephone System |
|
|
|
|
|
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Computer |
CPU |
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| USB |
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| IEEE1284 Parallel Data Bus |
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| IEEE 802.3 |
|
|
|
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| IEEE 1394 |
|
|
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| I/O Ports |
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| PC Card |
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| SCSI |
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Video Port |
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| LCD Monitor |
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Consumer Electronics
|
| Loudspeaker |
|
|
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Linear AC/DC Adapter |
|
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Electromagnetic Loads, Motor |
|
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Solenoid Protection |
|
✗ |
✗ |
✗ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note: The application summary is for reference only. Determination of suitability for a specific application is the responsibility of the customer.
Typical PPTC Circuit Protection Designs
The following are examples of typical circuits using Littelfuse PPTCs in combination with other Littelfuse circuit protection devices to provide a comprehensive protection solution. Contact a Littelfuse application expert for design assistance or visit www.littelfuse.com/designcenteror https://www.littelfuse.com/PPTCs for additional information. Be sure to to verify specifications and test device performance before use in the end application.
Power Over Ethernet

LI-ION Battery Pack

USB 1.1

USB 2.0

IEEE 1394 - Firewire

TIP/Ring Circuit - Metallic
